# TryHackMe Advent of Cyber
Every year since 2019 the cyber security platform TryHackMe (THM) has hosted an advent of cyber during the Christmas season that allows pen testers to complete challenges every day of advent. I decided this year to participate and this will be a blog post I will update each day with a new walk-through of the rooms.
Day 1.
Outline
Us as penetration testers have discovered a YouTube to MP3 website that has been reported as malicious, we decide to check it out since these types of websites are used for malware campaigns to distribute malware or perform mass phishing attacks.
The attack
We visit the website to be met with a box asking for a YouTube link to download the MP3, I supply a random video and get a zip file called "download.zip". This zip file contains 2 files "song.mp3" and "somg.mp3" a misspelt version of "song.mp3" designed to trick the user into running it instead of the "song.mp3".
I check the file types of each file to discover that "song.mp3" is an audio file BUT "somg.mp3" is an MS shortcut that executes powershell code.
I run "cat somg.mp3" to check the content and get a github link "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MM-WarevilleTHM/IS/refs/heads/main/IS.ps1". This leads to a simple stealer written in powershell.
I discover the C2 server located @ "http://papash3ll.thm/data".
From here I discovered a tag from the hacker "Created by the one and only M.M.", I search this on GitHub and discover a GitHub issue "https://github.com/Bloatware-WarevilleTHM/CryptoWallet-Search/issues/1" which someone called "MM-WarevilleTHM" opens.
I am pretty sure this is the mysterious M.M, I check their config file to find their name is "Mayor Malware".
Questions
1. I discover the author using Exiftool
2. I find the C2 server in the malware payload I discovered in the "somg.mp3"
3. I find M.Ms name using their GitHub config file
4. I find the issues using GitHub
Outro
This was a fun little room teaching penetration testers how important OPSEC is and how 1 small slip up can unravel your entire operation.
Day 2.
Outline
We as the SOC have been alerted of activity on our network and it is our job to find the cause of the issue and what has caused it.
The attack
First we navigate to the elastic portal given to us by THM and go to the discover tab
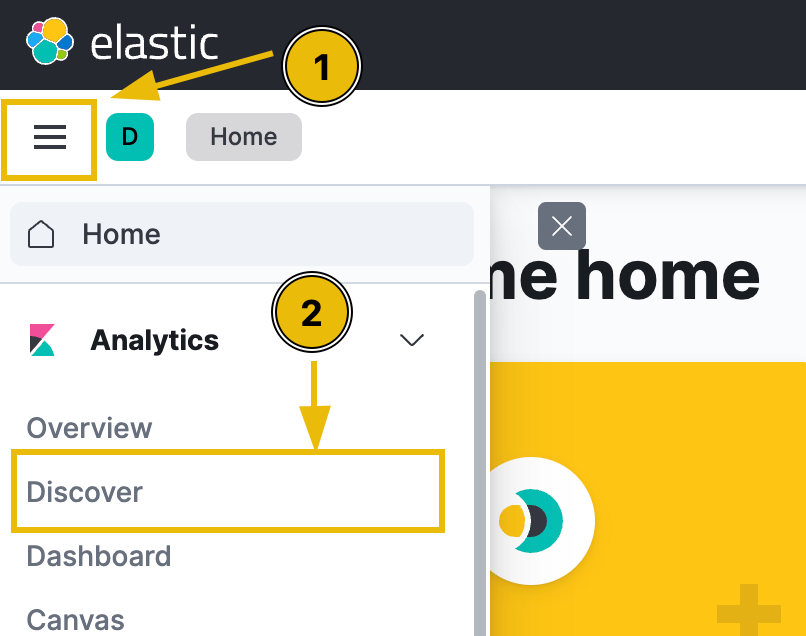
We are informed that the activity occurred on Dec 1st, 2024, between 0900 and 0930 so we set our time window to this and get 21 hits. The data at the moment is not very easy to read and we need to format it.
We apply filters to get the date, host, username, event type, command and the event outcome which allows us to see that an attacker has executed a powershell script on our system which immediately raises red flags for me.
We filter for authentication attempts and roll back to the 29th to be presented with a lot of access attempts that shows us an attempted brute force attack, we filter out our IP and are left with an attacker that successfully authenticated with a brute force attack.
However it seems this person gained access to the ADM-01 account with weak credentials that they then changed and forced an update for by using the powershell script that reboots the system.
Questions
1. The account with attempted login attempts is the account with the most access attempts
2. We filter to find the amount
3. We filter to find the IP
4. We filter to find the date
5. We decode the string in the powershell script
Outro
Overall this was a fun room that gives a basic insight into what SOC staff deal with and can allow people to dip their toes into this subject without fully committing yet.
Day 3.
Outline
We as penetration testers are given a Blue and red team task, we are told to investigate what has happened and discover the source and learn how RCE exploits can happen due to unsanitized file uploads.
The attack
Operation Blue
Similarly to yesterday we are using Elastic to check logs and today we are searching through Apache2 logs. We change our collection of logs to "wareville-rails", it shows us no results but that is because by default we are searching from the last 15 minutes. We change the time frame, starting at "**October 1 2024 00:00:00**" and going to "**October 1 23:59:59**".
We discover someone has sent requests and a file called "shell.php" has been accessed, this seems to be a web shell of some kind uploaded via an insecure file upload
We filter by the "shell.php" and get 11 hits.
Operation Red
In this section we are learning how web shells work, how file uploads can be exploited and how we can do so ourselves.
We navigate to "frostypines.thm" and are met with a website, we see a login tab and click on it. We do not have the credentials but we can guess using default credentials like "admin", after gaining access we find an admin panel at "/admin". We can create a new room which I do and for the image I upload a simple PHP RCE file. We go back to the normal website. navigate to the rooms, open the image in a new tab and voila we have a command bar we can use to run commands.
We run "ls" to find that the flag.txt is in the cwd so I "cat flag.txt" to get the flag file.
Questions
1. We find this in the logs when filtering for "shell.php" in the message
2. We find this in the logs when we filter for IPs
3. We find this after successfully uploading an RCE file and gaining a web shell
Outro
Overall I really enjoyed this room, it included some aspects from yesterdays room and it also taught us what web shells are and how they work.
Day 4.
Outline
Glitch has been revamping the towns security defenses by adding a firewall, patching vulnerabilities and discovering exploits that he then patched. Unaware of Glitchs good intent the SOC team launched an investigation into Glitch.
The attack
We will be identifying malicious attacks using the MITRE ATT&CK framework, we will learn how to use the Atomic Red Team tests to conduct a simulated attack.
First we use the ART to setup an phishing attack that goes by "T1566.001", we then have to detect it in the log. We find the event and navigate to it's path to which we find a file called "PhishingAttachment.txt" which contains a flag.
Answers
1. We find this in the path from the logs
2. Found on google
3. Found on google
4. Run "-ShowDetails" on T1059.003
5. Go to the path of the malware file found in the execution logs
6. Found in that file
Outro
Overall this room was a lot more difficult than other rooms, it posed a greater challenge but was also one of my favorite rooms because of my sense of accomplishment.
Day 5.
Outline
Software was finishing up some software and on his way home he sees a young boy looking sad, he asks "What would you like for Christmas?" the boy responded "I wish for a teddy bear, but I know that my family can't afford one.". This sparked an idea in Software's head, what if he made an app where everyone could share ideas and the mayor could help make them come true.
Them mayor immediately endorsed this idea, even chipping in to help but through the haste they left bugs in the software that we are going to find.
The attack
Today we are looking at XML and XXS vulnerabilities where entities can be exploited to pull down sensitives files that the parser will show.
When we navigate to the web page we are met with the wish list, we add an item to our cart and view our cart by proceeding to payment, we intercept the product.php request to find XML data being transmitted, we edit the payload to get the "/etc/hosts" file and we see that we can access that file with this showing that we can use an XXS exploit.
We craft a payload to get the wishes file we couldn't access earlier.
Answers
1. We find this by bruteforcing the wishlist path
2. We find this in the CHANGELOG path
Day 6.
Outline
Today we are doing malware analysis using sandbox tools, exploring how to use YARA rules to detect malicious patterns on a system, learn about malware evasion techniques and implementing our own evasion technique.
The attack
Today we learn how the registry can be used to detect sandbox environments and how to use floss to analyse strings from a malware exeutable.
Answers
1. Found after using the .\JingleBells.ps1
2. Found after using floss.exe to analyse the malware
Day 7.
Outline
Today we are analyzing AWS logs. A company called care4wares has had their donations stolen and it is our job to analyse the logs and find the source.
The attack
We are tasked with analyzing the cloudtrail log file and finding who or what is responsible for the lack of donations. We use jq to summarize the information into an easier to read format.
Answers
All answers are found from directly analyzing the log file with custom jq options.
Outro
Overall this was a challenging room, I got stuck a lot during this but it taught me a lot about AWS logs and JQ.
Day 8.
Outline
Today we are working with shellcode, reversee shells and fundamentals.
The attack
We are using msfvenom to generate a windows reverse shell using tcp, this will be ran on the victims machine to allow an attacker a tunnel into the victims network.
Answers
1. Sadly today I was unable to complete this task due to Windows defender flagging and removing the reverse shell, the attackbox and target being slow and overall being buggy.
Outro
Overall this room could've been fun but it was slow and buggy.
Day 9.
Outline
Today we are going over GRC ( Governance, Risk and Compliance).
The attack
We will be performing a risk assessment on given statements.
Answers
1. Found by completing the assesment
Outro
This was a very small room that just briefly went over GRC, just enough to understand.
Day 10.
Outline
In today's attack we are talking about phishing and file macros, understanding what both of them are and how macros can lead to attacks.
The attack
First we use Metasploit msfconsole to generate a malicious word macro file that will allow us a tcp reverse shell onto a windows system.
We log into the mail portal and compose an email to `marta@socmas.thm`, we attach the payload as a file and rename it to something more convincing like "receipt.docm" or "invoice.docm".
We listen using msfconsole `multi/handler` on the port we specified for the exploit, from the point we send the email we must wait for the target to execute the payload on their system.
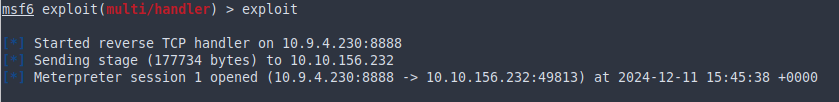
Yes! From this point we navigate to the administrators desktop and retrieve the flag.
Outro
Overall I loved this room, i'm a big fan of offensive security especially exploitation and enumeration. This room outlines the basics of meterpreter and how to create exploits
Day 11.
Outline
Today we are learning about exploits in wireless technologies.
The attack
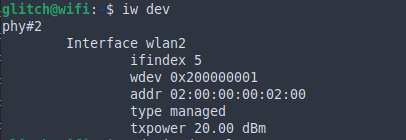
First we connect to the ssh server given to us, we find the wireless points available to us using the iw dev command
We then scan for nearby devices.
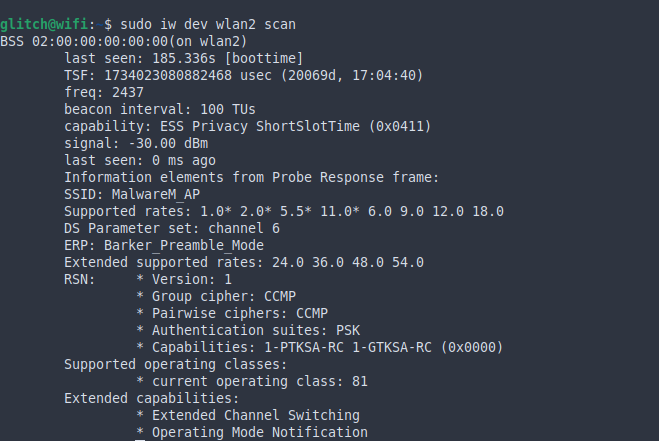
We change wlan2 to monitor mode and use airodump-ng to monitor the network. We send deauth packets to the network to force the client to have to reconnect to the network allowing us to get a handshake.
We use airocrack-ng to bruteforce the password.
Answers
1. Found using iw dev
2. Same as Q1
3. Same as Q2
4. Same as Q3
Day 12.
Outline
Today we have been called because a bank has had fraudulent transactions placed. We are exploring race conditions and timing attacks.
The attack
We use burpsuite or a script to quickly send multiple requests at the same time in parallel, a well made system should handle one at a time but this system is buggy leading each transaction to go through.
Answers
1. Found by successfully transferring 2000 to an account
Day 13.
Outline
Today we are exploring websocket vulnerabilities.
The attack
Unlike typical http connections websockets keep a connection open for 2 way data transmission.
We use burp suite to listen to the connections and change a value.
Answers
1. Found using message alteration
2. Found using message alteration
Day 14.
Outline
We are looking at certificates and self signed certs as well as using burp suite to intercept traffic.
The attack
First we modify our hosts file so we can visit the domain setup for the site.
We then use burp suite to listen for admin credentials.
Answers
1. Found by checking the certificate
2. Found by sniffing credentials
3. Found by hacking the elf account
4. Check the requests
5. Log into her account
Day 15.
Outline
Today we are going over active directory.
The attack
First we setup a new policy called password policy and configure its settings for us to exploit. We check powershell logs, active directory and event log to find the answers to our questions.
Answers
1. Found in the event logs
2. Found in the same event
3. Found in the powershell logs
4. Found in event logs
5. Found in event logs
Day 16.
Outline
Today we are going over Microsoft Azure. Why Azure is used, the authentication services and the cloud shell
The attack
We sign into the Azure lab and launch the Azure CLI.
We run `az ad signed-in-user show` to show the signed in user. We list the users with `az ad user list`.
We list the groups and discover a Secret Recovery Group that we log into.
We list the key vaults with `az keyvault secret list --vault-name warevillesecrets`
Answers
1. Found by listing the groups
2. Found by listing the groups
3. Found using the groups
Day 17.
Outline
Toady we are going over log parsing, SPLs and more.
The attack
We open the splunk portal and select `Search and Reporting` and proceed to search with `index=*` over `all time`.
We create a new field and name each part of the logs.
Answers
1. Found by filtering the logs
2. Same as 1
3. Same as 1
Day 18.
Outline
Today we are learning about AI and prompt injection.
The attack
We find out about queries like query:info and more. We use a Prompt injection to get an RCE. We setup a tcp listener and send it a reverse shell link which the system will execute allowing us RCE.
Answers
1. System prompt
2. Use query inputs
3. Perform a prompt injection
4. Get an RCE shell
Day 19.
Outline
Today we are learning how to interact with executable apis, modify apis with frida and hacking a game.
The attack
We use frida trace to trace the libgame.so file and find the otp js file, we add a log item so we can see the code generated, we use this in the game and get the first flag.
We then progress and find another penguin which we can buy the flag from, we open the purchase javascript file, we set the value to ptr1 which allows us to purchase the flag.
Similar to part 2 we set the retval ptr to 1.
Answers
1. Found by completing part 1
2. Found by completing part 2
3. Found by completing part 3
Day 20.
Outline
Today we are analyzing network traffic using wireshark, identifying indicators of compromise and how C2 servers work.
The attack
We open the pcap file and start looking around. We find some post requests using http to an external server, we analyze these packets and discover C2 commands.
Answers
1. Found by analyzing packets
2. Found by checking the IP connected
3. Same as 1
4. Same as 1
5. We get the key in a request and learn we need to use AES ECB, we then find the encrypted string and decrypt it using cyberchef
Day 21.
Outline
Today we are doing reverse engineering, we will be understanding the structure of a binary file, the difference between disassembly and decompiling, multi stage binaries and reversing multi stage binaries.
The attack
We will be decompiling 2 .net binaries. The first we will need to use PE studio since it is a windows executable to get key information about this application. We then use ILspy to decompile the code into a more readable format.
We now will be doing this on the `WarevilleApp` file. First we use PE studio to get key info from the app, this turns out few results so I decompile the app using ILSpy, I find a lot of key information using this.
Answers
1. Found by decompiling `WarevilleApp.exe`
2. Same as 1
3. Same as 1
4. Found by downloading the malware and using ILSpy to decompile it
5. Same as 4
Day 22.
Outline
Today we learn about Kubernetes, DFIR and log analysis.
The attack
We start a K8S with `minikube start` we then wait about 3 minutes before listing the pods with `kubectl get pods -n wareville`.
After starting the cluster and ensuring all pods are up we can enter a pod shell with `kubectl exec -n wareville naughty-or-nice -it -- /bin/bash`, then we check the apache log with `cat /var/log/apache2/access.log` for me I didn't have anything so I checked the error logs.
We then check the docker ps and run an ls with `docker exec ID ls -al /var/log` we find logs that are stored in `/home/ubuntu/dfir_artefacts/docker-registry-logs/log` which we sort with `cat docker-registry-logs.log | grep "HEAD" | cut -d ' ' -f 1` so we can see all the IPs that connected
Answers
1. All found by checking logs
Day 23.
Outline
Today we are doing hash cracking as personal favorite attack of mine.
The attack
First we use john the ripper to crack the hash in hash1.txt.
Now we use `pdf2john.pl` to convert the pdf file to a hash and then crack it.
Answers
1. Found by cracking hash1.txt
2. Found by cracking the pdf file
Day 24.
Outline
On Christmas eve we lay out our stockings for Santa, but for SOC engineers they can never rest, for foes lie around every corner. Today we are learning about MQTT traffic
The attack
First we start wireshark and listen on the any interface, then we navigate to `Desktop/MQTTSIM/walkthrough` and run `walkthrough.sh` to learn.
We then follow the first step and launch the `challenge.sh` file. We then find the light on packet and post it back